|
LAM SON 719 by Maj. Gen. Nguyen Duy Hinh Published by U.S. Army Center Of Military History
Contents
Glossary
LAM SON 719
CHAPTER IV
The Offensive Phase
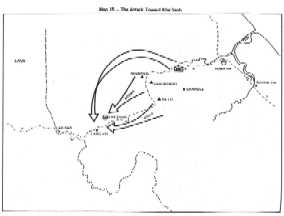
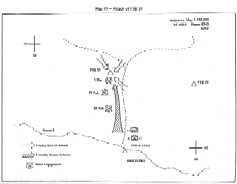
Preparing to Cross the BorderTo assist I Corps forces in making preparations for their cross- border offensive, XXIV Corps implemented Phase I of LAM SON 719 exactly as scheduled, at 0000 hours on 30 January 1971. Codenamed DEWEY CANYON II, this operation consisted of securing staging and assembly areas for I Corps units in the northwestern corner of Quang Tri Province adjacent to the Laotian border, including Khe Sanh Base and Route N÷ 9. As part of a deception plan, the U.S. 101st Airborne Division (Air mobile) launched heavy attacks by fire and reconnaissance patrols into the A Shau valley farther to the south. This move was to divert the enemy's attention from the area where the main action was about to unfold.
The U.S. 14th Combat Engineer Battalion immediately followed the
attacking cavalry forces, restoring nine of the eighteen required
bridges and nine of the 20 required culverts along the road. At
Khe Sanh, U.S Army engineers were to survey a site planned for an
assault airstrip which was to run parallel to the old,
unserviceable PSP airstrip. This assault airstrip, scheduled to be
completed on 3 February, was to be
Initial artillery support was provided by the 1/82 (-) and 2/94 Artillery Battalions at Vandegrift along with the 8/4 Artillery Battalion at Camp Carroll. The 5/4 Artillery Battalion was expected to displace forward to provide support at Khe Sanh. Beginning at 0830 hours, three infantry battalions (3/187 Infantry, 1/11 Infantry and 4/3 Infantry) of the U.S. 1st Brigade 5th Infantry Division (Mechanized) were heliborne into three landing zones in the Khe Sanh areÕ The operation proceeded smoothly and was completed at 1530, each battalion moving into its assigned area of operation without significant contact with the enemÜ While the 1/11 Infantry Task Force secured Khe Sanh, the 1/77 Arrored Task Force remained in the Vandegrift area and provided security along Route N÷ 9 from the Rockpile to the south of Vandegrift. The 1/1 Cavalry Task Force meanwhile conducted a reconnaissance in force along from Khe Sanh toward the Laotian border. After U.S. armored and infantry forces had consolidated their positions in the objective area on 1 February, heavy artillery elements long with the 8/4 Artillery Battalion began to move into Khe Sanh. On that day, U.S. engineer units also completed temporary repairs on the road from Vandegrift to Khe Sanh and it was now able to accommodate tracked vehicles as far west as Lang Ve¸ The 27th Engineer Battalion meanwhile began to remove damaged PSP from the main airstrip at Khe Sanh.
Two efforts were conducted in the next morning; the 1/1 Cavalry
Task Force advanced to approximately four kilometers west of Lang
Vei where it established screen near the border. Mean while, the
2/17 Cavalry Squadron conducted a raid in an area where enemy
presence was suspected, approximately 18 kilometers south of Khe
Sanh. No enemy contact was made but they did find a hospital
located in a large tunnel complex. Evidently the enemy had moved
out 12 to 24 hours earlier.
On 2 February, the first combined operational meeting was held at the headquarters of I Corps Forward, attended by all RVNAF and U.S. commanders and detailed operational orders were issued. Immediately after this meeting, ARVN units feverishly completed their preparations for the big operation that promised numerous challenges. The next day, the 1st Ranger Group (21st, 37th and 39th Ranger Battalions) was helilifted into the Phu Loc area northwest of Khe Sanh to defend a fire support base to be established ther©
The 2d ARVN Airborne Brigade arrived at the Dong Ha airfield on 6
February while other ARVN units - the 1st Armor Brigade, 1st
Airborne Brigade and 3/1 Infantry Regiment - moved overland to the
Ham Nghi (Khe Sanh) areÕ Upon arrival, the 1st Armor Brigade and
the 1st Airborne Brigade, which were both scheduled to move out by
way of Route N÷ 9 on DDDay Phase II, immediately entered the
assembly area adjacent to the border. That evening, a regrettable
incident occurred. A United States Navy aircraft mistakenly
attacked the ARVN forward elements destroying one M-113 armored
personnel carrier; additionally, six ARVN
On the logistic side, immediately following in the steps of the U.S. engineers who were repairing and opening roads, U.S. logistic units were displacing forward to establish support facilities and Forward Support Area (FSA) 26-1 at Ca Lu south of Vandegrift was opened on 30 January. Advance elements of Forward Support Area 26- 2 arrived at Khe Sanh on 3 February and this facility was operational two days later. Ground transportation soon became difficult because the road section between Vandegrift and Khe Sanh was only trafficable one waÜ Despite this, U.S. and ARVN convoys, combat and logistic alike, moved day and night. During the first days, and as originally planned, ARVN units were supported by U.S. logistic facilities. As soon as ARVN units reached the assembly area, they were issued supplies in preparation for action. This activity proceeded smoothly except for some difficulties in the issue of combat rations. Vietnamese combat rations were not similar to American C-rations. Instead of a self- contained package of individual meals, each Vietnamese ration consisted of three separate items: instant rice, canned meat or fish, and condiments. These were packaged individually but issued collectively by the carton. American logistics personnel were unfamiliar with these rations and with ARVN issue and accounting procedures so to solve the problem some Vietnamese specialists were detached to FSA 26-2. During this same period, ARVN logistic units dispatched advance teams to Khe Sanh to establish their own support facilities including ammunition and fuel supply points, which were scheduled to initiate operations on D- Day + 17 (16 February).
Probably taken by surprise, enemy troops in Quang Tri reacted very
slowly and weakly during the first days. Although some mine
explosions occurred along the routes of advance, floating mines
appeared on the Cau Viet River, and a few rockets were fired into
rear support bases, other activities of Communist units in northern
Quang Tri Province showed no significant changes. The northwestern
corner of Quang Tri, in particular, remained very quiet.
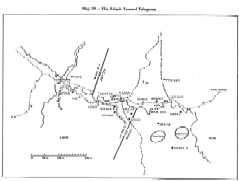
Securing Ban Dong
All supporting firepower provided by U.S. forces was coordinated by the U.S. 108th Artillery Group. The 155-mm and 8-inch howitzers and long-range guns hit against deep targets in lower Laos beginning at 0800 hours. The 108th Group expertly and effectively performed its support mission.
Meanwhile, U.S. air cavalry teams expanded their range in search
of the enemÜ Toward the north, not far from the border, by a
stream
While armored and infantry forces were progressing into Laos along the road, the northern and southern flank security elements were heliborne. The 4/3 Infantry Battalion was transported to Landing Zone Hotel in the Co Roc area by helicopters at 1100 hours without enemy contact. The 2d Airborne Battalion reached Landing Zone 30 ten kilometers north of Route N÷ 9 unhampered. At 1300 hours, however, near Landing Zone Ranger South, five kilometers northwest of LZ 30, the 21st Ranger Battalion's insertion was met with fire from 12.7-mm antiaircraft machine-guns; 11 rangers wounded and the troop insertion continued while U.S. air cavalry attacked the gun positions. This U.S. gun-ship activity resulted in a number of enemy troops killed and several trucks destroyed, but more significantly, these attacks caused numerous secondary explosions from a network of fortifications which lasted over a period of an hour. At 1620 hours, the 1st and 2d Battalions of the 3d Infantry Regiment were helilifted into two areas in the vicinity of Landing Zone Blue, four kilometers southwest of LZ Motel. Immediately thereafter, the 2/3 Battalion was engaged by the enemÜ Friendly forces sustained five wounded while the enemy lost nine killed and one 12.7-mm machinegun, one AK-47 assault rifle and one Chicom radio captured. At 1655 hours, U.S. air cavalry gun-ships attacked a suspected target two kilometers east of Landing Zone 31 causing numerous secondary explosions with flames reaching 1,500 feet in the air. Reconnaissance aircraft reported the fire lasted until just before daylight the following morning. After the attack on this target, the 3d Airborne Brigade Headquarters and 3d Airborne Battalion occupied Landing Zone 31 unopposed.
Toward nightfall, near Fire Support Base Phu Loc at the border,
the command post of the 1st Ranger Group and the 37th Ranger
Battalion were
By nightfall of the first day, the ARVN armored column had moved nine kilometers into Laos. Though enemy resistance was weak, the column could not move more rapidly because of the bad road conditions and the dense jungle on both sides of the road. During the day, on the Vietnamese side of the border, U.S. units continued to expand their operations to consolidate security for ARVN rear bases. The pioneer road from the Rockpile to Khe Sanh was opened to track vehicles by 1635 hours providing another vehicular access to Khe Sanh. In support of the first day of the cross-border operation, U.S. forces had flown 11 B-52 sorties expending 719 tons of bombs which caused 40 secondary explosions, and performed 468 helicopter gun- ship and 52 tactical air missions, destroying 11 gun emplacements and 40 trucks, damaging 18 trucks and causing 13 secondary explosions and 23 fires. Four huge "commando vault" bombs had been used to clear landing zones. During the night, C-130 gun-ships had also destroyed additional enemy trucks moving near Ban Dong, the next objective. On 9 February, the weather suddenly became very poor. Heavy rain made the road a quagmire, preventing the engineers from working. Heliborne troop insertions were delayed and logistical buildup efforts were halted. Those units already in Laos endeavored to consolidate their positions or increase the range of their patrols. Throughout the day, there were only two minor contacts made by the 21st Ranger Battalion near the Ranger South area and by the 8th Airborne Battalion north of Landing Zone Alpha approximately 10 kilometers west of the border with insignificant results reported by each unit.
The next day, 10 February, the weather improved but did not permit
heliborne operations until late in the afternoon when the 4th
Battalion, 1st Infantry Regiment, completed an assault into Landing
Zone Delta, 10 kilometers due west of LZ Hotel at 1630 hours. The
armored thrust meanwhile resumed at a stronger pace after a day of
marking tim© At 1700 hours the 9th Airborne Battalion was
inserted into Landing Zone A
The same day was marked by several other events. Troops of the 3d Airborne Battalion, operating approximately one kilometer east of Fire Support Base 31, were engaged by the enemy at 1230 hours. They suffered light casualties but captured six Molotova trucks loaded with ammunition. Extending their search north, this team found a cache of fourteen 82-mm mortars, four 122-mm rocket launchers and nine AK-47 assault rifles. Meanwhile, near the area of operations of the 21st Ranger Battalion, a flight of four VNAF helicopters bound for Landing Zone Ranger South was hit by enemy 37-mm antiaircraft artillery fire at 1300 hours. Two helicopters were downed and all passengers were presumed killed. The first helicopter carried two ARVN colonels, the G3 and G4 of I Corps. The second helicopter reportedly carried a number of foreign correspondents. It was suspected that the I Corps G3 had carried with him an operational map of LAM SON 719 along with signal operating instructions and codes. The loss of these documents to the enemy would be extremely significant. A thorough search of the area for the downed helicopters produced no results.
The linkup on Route N÷ 9 between the armored and airborne troops
at Landing Zone A Luoi (Ban Dong) nearly 20 kilometers deep into
enemy territory was an encouraging achievement. I Corps
Headquarters therefore decided to push the operation further
westward. Reinforcements were to be sent on 11 February to
increase security on the northern and southern flanks before
further advance was mad© At 1430 hours, the 311 Infantry
Battalion was heliborne to be inserted into Landing Zone Yellow but
because of last minute intelligence reports of important enemy
concentration nearby, the battalion was diverted to Landing Zone
Don, four kilometers southwest of LZ DeltÕ During the same
period, toward the north, the 39th Ranger Battalion was deployed in
the area of Landing
In order to obtain additional fire support for the planned movement all major fire support bases were consolidated and reinforced. At Fire Support Base 30, one 105-mm battery and one 105-mm battery were deployed. Fire Support Base 31, the command post of the 3d Airborne Brigade, had a six-piece 105-mm battery. Light bulldozers were helilifted into these fire support bases to help fortify the defenses. Fire Support Base A Luoi (Ban Dong), Fire Support Base Hotel of the 3d Infantry Regiment, and Fire Support Base Delta of the 1st Infantry Regiment (1st Infantry Division) also received an adequate number of artillery pieces. From 11 to 16 February, while I Corps staff in the rear was planning the next moves, ARVN units in the forward area in lower Laos expanded their operations and continued the search for the enemy, increasing the number of contacts and caches uncovered. In the ranger's area, on the northern flank, the 37th Ranger Battalion operating near Fire Support Base Phu Loc and protecting the northwestern approaches to Khe Sanh was continuously subjected to enemy attacks by fire and probes. At 1100 hours on 12 February, the battalion, supported by U.S. gun-ships, engaged an enemy force three kilometers north-northwest of the bas© The results were as follows: on the friendly side, four rangers killed, six wounded, and one UH-1G helicopter shot down by 12.7-mm fire; enemy troops suffered 13 killed, one captured and ten AK-47 assault rifles seized.
The 39th and 21st Ranger Battalions, which operated around Landing
Zones Ranger North and Ranger South respectively, were probably the
units most frequently in contact with the enemÜ At 1825 hours on
11 February, the 21st Ranger Battalion engaged the enemy four
kilometers northeast of its base killing 11 Communist troops, but
later, at 2200 hours suffered six wounded from an enemy attack by
fire consisting of forty 82-mm mortar rounds. During the afternoon
of 13 February, the 39th Battalion engaged a large enemy force at
three kilometers west-southwest of Landing Zone Ranger North,
killing 43 enemy personnel and seizing two 37-mm antiaircraft
artillery guns, two 12.7-mm machineguns, a substantial amount of
ammunition and assorted types of equipment.
In the area of operations of the Airborne Division, no additional major units were inserted after the initial deployment but the ones already in place were expanding their search activities. The 1st Armored Brigade launched two reconnaissance missions of combined armored/airborne forces north and south of Fire Support Base A Luoi (Ban Dong). In the afternoon of 11 February, the northern element engaged an unknown size force Friendly losses were two M-113 armored personnel carriers destroyed) one killed and one wounded. At approximately the same time) another M-113 detonated a mine, causing nine wounded. In the afternoon of 15 February, an element of the 17th Armored Squadron came upon two Russian trucks three kilometers north of Ban Dong and destroyed an estimated six tons of ric© Around Fire Support Bases 30 and 31, the 2d and 3d Airborne Battalions pushed further out. Their companies made sporadic contacts and proved superior to enemy forces in the areÕ In the morning of 12 February in particular, an element of the 2d Airborne Battalion engaged the enemy five kilometers southeast of Fire Support Base 30, killing 32 enemy troops, seizing 20 individual weapons and destroying three crew-served weapons. Friendly forces had only three killed. Other sporadic contacts were all in favor of friendly forces. At 1430 hours on 14 February, Fire Support Base 31 received an attack by fire which resulted in six airborne troops killed, three wounded and one bulldozer damaged. The following day, toward noon, Fire Support Base 31 received 122-mm rockets which killed two and wounded four.
In the meantime, south of Route N÷ 9, the 1st Infantry
Division introduced more troops into action. The 3/1 Battalion had
been transported to Landing Zone Don in the afternoon of 11
February, and the 2/1 Battalion was helilifted to Landing Zone
Delta 1, six kilometers southeast of Ban Dong, in the afternoon of
the following day to push further west. On 16 February, the 2/3
Infantry Battalion was inserted
Throughout this period, various units of the division searched for the enemy and made many contacts which produced substantial results to include several enemy caches. At 1615 hours on 11 February, the 311 Battalion observed a target one kilometer southeast of Landing Zone Don which had been hit by air-strikes. The battalion discovered 23 enemy bodies and seized two 12.7-mm machineguns, four AK-47 assault rifles and one chicom radi÷ In the afternoon of 12 February, this battalion found a cache three kilometers south- southwest of Landing Zone Don which contained 600 individual weapons, 400 82-mm mortar rounds, numerous rounds of assorted ammunition and the bodies of 50 enemy troops killed by air-strikes. Late in the afternoon, at three kilometers south of Landing Zone Don, the 1/1 Battalion discovered an enemy camp containing substantial amounts of food along with military clothing, equipment and ammunition, particularly 12.7-mm rounds. On 13 February, the 3/1 Battalion found another cache with thirty 75-mm recoilless rifles, fifty 55 gallon drums of gasoline and substantial quantities of other types of equipment. At the same time, six kilometers north- northeast of Landing Zone Grass, the 2/3 Battalion seized three new Russian trucks.
As of 13 February, contacts being made by elements of the 1st
Division forces were increasing. During the afternoon of that day,
the 1/1 Battalion engaged an enemy element three kilometers south-
southwest of LZ Don, killing 28 enemy troops and seizing a storage
area which contained an East German machinegun, seven RPDs, one
B40, one B41, two SKS, gasoline, generators and huge quantities of
food along with kitchen utensils. On 14 February, the 2/3 and 1/3
Battalions each received an attack by fire of an estimated one
hundred 82-mm mortar rounds. The 1st Battalion had one killed and
seven wounded and the 2d Battalion had 16 wounded. Even though
enemy attacks by fire and actual contacts increased during the
next few days, all the units of the 1st ARVN Division continued to
seize substantial amounts of enemy supplies and materiel.
In addition to the big guns of the 108th Artillery Group, U.S. air
support was an important factor during the first week of the
incursion. Each day, from 500 to 800 sorties of air cavalry gun-
ships were flown in addition to approximately 100 sorties of
tactical bombers and, depending upon available targets, a number of
missions by B-52 strategic bombers. Losses inflicted on the enemy
by these air-strikes were very significant(3). But despite the devastating U.S. air
and artillery support, enemy anti-aircraft gunners took a heavy
toll of helicopters; and the U.S. air cavalry, as well as the
RVNAF, had to increase their efforts to silence the Communist guns.
According to the operational plan, the Airborne Division and the
1st Infantry Division were expected to advance westward, each step
forward to be solidly anchored on a fire support bas© The
planners of LAM SON 719 apparently believed that this tactic,
coordinated with the massive support by the USAF and U.S. Army air
cavalry, would help accomplish the mission with minimum losses.
But because of this procedure, the operation progressed slowly and
did not exactly meet the expectations of U.S. counterparts. In
Saigon, General Abrams, COMUSMACV, in a discussion with General Cao
Van Vien, Chairman of the JGS/RVNAF, expressed his wish to see the
operational units reach Tchepone as quickly as possible(4). Then, in the afternoon of 16
February, in the forward command post of I Corps at Dong Ha
airfield, Generals Vien and Abrams met with Generals Lam and
Sutherland for two-and-a-half hours. After a review of the general
situation, a decision was made to step up the operation by having
the 1st Infantry Division quickly occupy the higher mountain tops
south of the Xepon River and establish fire support bases there to
support the Airborne Division1s push toward Tchepone. They
estimated that this would take three to five days. But, as later
events were to prove, battlefield developments seldom occur exactly
as planned. Enemy reactions were becoming stronger with each day
and the test of strength more arduous.
The Enemy CounteractedNearly a week had passed since Ban Dong was occupied. Except for a few clearing activities conducted by units of the 1st Infantry Division, the forward movement of ARVN forces seemed to have stalled. The heliborne insertion of troops through the fierce enemy air defense screen in the afternoon of 10 February had enabled friendly forces to quickly occupy this objective. The linkup with armored forces had also been made immediately thereafter. Fire Support Base Ban Dong was now well entrenched with six 105-mm and six 155-mm howitzers and adequate ammunition and supplies. However, as of 16 February, six days after the capture of Ban Dong, there had been no further progress by ARVN troops toward the objective Tchepone. In the meantime, the enemy had increased his air defense capabilities along the mountain slopes to the south. Enemy attacks by fire, which were initially conducted with assorted mortars and 122-mm rockets, were now occasionally augmented by long-range artillery. ARVN armored units had tried to advance but could not make much progress. The dense forests bordering the road required careful, time consuming reconnaissance to avoid ambush and this made the armored column's movement extremely slow.
On 17 February, it rained hard and the helicopters rested idly on
the airfields. However, since early morning, an armored infantry
task force consisting of the 17th Armored Squadron and the 8th
Airborne Battalion operating north of Ban Dong had been engaging
the enemÜ The results were four friendly troops killed while the
enemy suffered 36 killed. Sixteen AK-47 assault rifles and a
quantity of military clothing and equipment were seized. Toward
noon, this task force made another contact four kilometers north
of Ban Dong and captured one PT-76 amphibious tank, two Russian
trucks, one 12.7-mm machine gun and two 7.62-mm machineguns. The
PT-76 tank was only slightly damaged and was towed back to A Luo¸
To the south, the 1st Infantry Division continued to make contacts
and receive attacks by fir©
All these activities were quickly eclipsed by reports of heavy enemy troop concentrations around the 39th and 21st Ranger Battalions. Both battalions were being subjected to attacks by fire and ground attacks and the fighting lasted all night while friendly artillery, tactical air and flareships responded quickly in support of the embattled rangers. The next morning, enemy pressure on the 21st Ranger Battalion gradually diminished but heavy pressure persisted on the 39th Battalion in the Ranger North areÕ The battle continued over 19 February. Enemy troops here were confirmed to be elements of the 102d Regiment of the 308th Division, all with new weapons and clothing. Before launching an assault, the rangers reported, the enemy made extensive use of recoilless rifles and mortars; his fire was very accurate. The strongest enemy attacks were directed at the eastern flank of the rangers which was their weakest spot. However, the 39th Battalion continued to hold its positions with support from U.S. artillery and tactical air.
Meanwhile, information concerning the enemy's growing capabilities
became clearer with each daÜ His air defense network was becoming
dense and heavy artillery was committed. ARVN artillery-men
confirmed that, in addition to the various types of mortars and
rockets commonly
Enemy main force units in the area of operation were confirmed during the fir8t days to be the 1st Regiment of the 2d (Yellow Star) Division, 24B Regiment of the 304th Division and elements of the 675th Artillery Regiment. A prisoner from the 14th Air Defense Battalion of the 2d Division disclosed that the subordinate units of this division (1st, 3d and 141st regiments) had been moving east from the Tchepone area since early February to block the ARVN advance. Enemy opposition grew stronger with each day around Ban Dong and the area of Route 1032B for which the rangers were responsible. On 10 February, the 21st Ranger Battalion engaged an element of the enemy's 88th Regiment. The next day, the 37th Ranger Battalion engaged a battalion size unit near FSB Phu Loc. The discovery of the command post of the 308th Division on 18 February further confirmed reports that this division had joined in the fighting (the 308th Division had three regiments: 36th, 88th and 102d).
During the night of 19 February, the enemy continued to attack the 39th Battalion while launching uninterrupted attacks by fire to hold the 21st Battalion in check. Seven fixed wing gun-ships and six flare-ships were used in support of the 39th Battalion and, from 0730 to 1430 hours on 20 February, 32 tactical air sorties were flown in support of the rangers. Efforts to resupply and evacuate their casualties were made with strong support from tactical air, gun-ships and artillery. Some helicopters managed to land in the area, ammunition was delivered and some wounded evacuated. But upon takeoff, two helicopters were damaged by enemy fir© One had to land in the positions of the 21st Ranger Battalion (Ranger South) and the other managed to land at Fire Support Base 30.
In the afternoon, reconnaissance aircraft reported sighting an
estimated 400 to 500 enemy troops encircling the 39th Battalion. At
1710 hours on 20 February, radio contact with the 39th Ranger
Battalion was lost. At 1856 hours, I Corps CP received information
that the able bodied personnel of the battalion had fought their
way out and reached the 21st Ranger Battalion positions with most
of the wounded and all of their weapons but with very little
ammunition left. Those who reached the 21st Ranger Battalion
numbered nearly 200; 107 were still able to fight but 92 were
wounded. Total losses were 178 dead and missing and 148 wounded.
Intelligence reports indicated enemy casualties to be 639 killed
with a corresponding number of weapons destroyed (423 AK-47s, 15
B40/B4ls and numerous automatic weapons).
While the 39th Ranger Battalion was holding out, numerous activities took place in other areas. U.S. air cavalry continued to search for and destroy pipelines. Units of the 1st Infantry Division moved further south, striking along Route 92 and finding a number of enemy installations, but also making numerous contacts and receiving attacks by fir© The 8th Airborne Battalion and armored elements engaged the enemy two kilometers north of Ban Dong, destroying one T-34 tank and a 23-mm gun position. This was another strong indication of enemy armor involvement. On the friendly side, a number of U.S. helicopters were shot down while on supply, medical evacuation or support missions. The corps commander had concluded that the position held by the 21st Rangers and the survivors of the 39th was untenable. A maximum effort in air and artillery support was required for each re-supply and evacuation mission and he had other pressing demands for this support. The position was not an objective in itself and there was no military advantage in sacrificing a ranger battalion in a doomed attempt to hold it. The corps commander was looking toward his objectives in the west and he wished to conserve as much of his combat power as possible for the main mission.
In the southern sector of the 1st Division, within objective area
A-Ro, the 2/3 Battalion came into heavy contact with the enemy on
23 February. The 3/3 Battalion was brought in to reinforce but
the enemy would
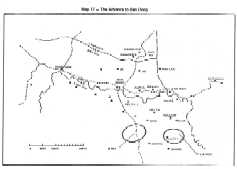
The loss of Fire Support Base 31The withdrawal of the 21st Ranger Battalion left the northern flank of the Airborne Division exposed and Fire Support Bases 31 and 30 now bore the brunt of enemy attacks. They had been under pressure since the 2d and 3d Battalions of the 3d Airborne Brigade were inserted. Established in the immediate vicinity of the Communist north-south supply line, both bases were able to monitor closely enemy troop movements as well as signs of enemy armored activities. Each battalion left but a small force to defend the bases while a larger force fanned out in security and search activities, but this mobile force was not sufficient to prevent the enemy from moving close to the bases and setting up mortars and antiaircraft guns to interdict supply and medical evacuation attempts(5). Each helicopter landing or departing usually resulted in heavy attacks by fir©
A company of the 3d Airborne Battalion operating southwest of FSB 31 received a rallier who was a sergeant, platoon leader in the 24B Regiment of the 304th Division. He reported that the Communists had been preparing to counter the RVNAF-US operation since October 1970. Rear service units of Group 559 had in fact received orders to prepare for combat and an army corps size headquarters called the 70th Front was designated in October 1970, to command the 304th, 308th and 320th divisions, a number of artillery regiments, an armored regiment, a number of air defense regiments and other support units. To counter Operation LAM SON 719, the 70th Front Headquarters was sent to lower Laos along with NVA combat units. The 24B Regiment along with advance elements of the 9th and 66th Regiments had infiltrated the border area west of Quang Tri since 9 February. From all these new revelations it appeared that the enemy would make a determined effort to defend his base areas.
The situation heated up following the evacuation of ranger
positions in the north and as a result of heavy enemy attacks. The
31st and 32d Companies, 3d ABN Battalion operating in the mountain
ranges northeast of Fire Support Base 31 received orders from the
division to move south and meet an armored task force composed of
the 17th Armored Squadron and two companies of the 8th Airborne
Battalion coming
At 1100 hours on 25 February, Fire support Base 31 received
massive attacks by fire, including fire from 130-mm field guns. At
1300 hours, the 31st Company to the south reported enemy armored
movements. The base responded with artillery fire and called for
artillery support from Fire Support Bases 30 and A Luo¸ The
forward air controller's aircraft (FAC 229) was not in the air
because of a confusion in grid coordinates and did not arrive until
1400 hours. By that time, fire from small weapons was being
received from all directions and enemy tanks had reached the
southern perimeter of the bas© The first flight of fixed wing
tactical aircraft to reach the base destroyed a number of enemy
tanks on the spot and held back the armored thrust against the
southern perimeter. At 1520 hours, an estimated 20 tanks supported
by enemy infantry troops moved in from the northwest and the east.
At precisely the same time, an F-4 aircraft was hit and erupted in
flames but the pilot ejected. The Hammer FAC aircraft left its
position to direct effort to rescue the U.S. pilot, interrupting
air support for Fire Support Base 31. After a fierce artillery
barrage, the enemy assaulted. At that time, a helicopter of the
advisory team for the Airborne Division was the only aircraft
flying overhead. It turned its M-60 machinegun fire on the enemy
but it was in vain! Artillery from A Luoi and Fire Support Base 30
continued to fire in support but could not stop the enemy tanks
attacking on the hill slopes. Forty minutes later, the base was
overrun. It is possible that had the FAC remained
Between 25 February and 1 March, on its way to relieve Fire Support Base 31, the armored-infantry task force composed of the 17th Armored Squadron, the 8th Airborne Battalion and remaining elements of the 3d Airborne Battalion fought three major battles on 25 February, 27 February and on the night of 1 March 1971. They lost 27 KIA, 186 WIA, one MIA, three M-41 tanks and 25 armored vehicles destroyed. The enemy sustained 1,130 killed, two captured, over 300 assorted weapons seized, 17 PT-76 and six T-54 tanks and two Molotova trucks destroyed. The prisoners disclosed that the 24B Regiment and the 36th Regiment of the 308th Division, reinforced by the 202d Tank Regiment, had taken part in recent battles. The 24B Regiment was the unit which attacked Fire Support Base 31 while the 36th Regiment was operating to the south. Cumulative enemy losses during these battles equaled one half of the strength he initially committed.
Even before the attack on Fire Support Base 31, Fire Support Base
30 of the 2d Airborne Battalion had been the target of repeated
enemy attacks by fire involving all sizes of ammunition in the
Communist inventory. Because of the accurate enemy anti-aircraft
fire, helicopter takeoffs and landings were very riskÜ Each
resupply mission was
Up to this point, the direction taken by enemy reactions seemed rather clear. The main forces committed consisted of the 304th, 308th and 2d (Yellow Star) Divisions along with elements of the 320th and 324B Divisions and armored and artillery units. The NVA strategy appeared to concentrate on massing the infantry, armor and artillery force necessary to isolate and overwhelm - one by one - the RVNAF fire bases. The enemy took advantage of the rugged terrain to disperse his logistic, engineer and air defense units into small elements which were well entrenched in fortified positions established throughout the area and ARVN forces made contact wherever they moved; only by summoning concentrated firepower were they able to overpower the enemÜ The enemy appeared to have coped effectively with friendly mobile forces, heliborne insertions of troops and artillery positions. His mortar fire, which was sustained by adequate reserves of ammunition, was now supplemented by long-range artillery. This came as a new experience for ARVN forces who were not fully prepared to cope with massive and sustained attacks by fire and the conventional armor supported infantry attack that overran FSB 31 was probably the first Communist large scale combined arms attack in the Indochina theater. The difficulties that Fire Support Base 31 had experienced and Fire Support Base 30 was now experiencing showed that enemy reactions largely consisted of attacks by fire and air defense. Attacks by fire were designed to create tension and cause attrition. Anti-aircraft fire was aimed at disrupting communications, supply and medical evacuation by helicopters, and isolating the bases.
On the friendly side, several shortcomings were evident from the
very beginning of the operation. First, high level headquarters
were located too far from the combat zone and from each other. As
a result,
Third, the U.S. XXIV Corps had no representative in the forward area with authority to coordinate the activities of those units supporting the RVNAF forces such as the 101st Aviation Group, the 1/5 Mechanized Brigade, and the 108th Artillery Group. All these units communicated directly with the ARVN divisions they supported. As a result, coordinating the allocation of support assets among the ARVN divisions became extremely difficult. The divisional advisory staffs meanwhile had no authority to handle the coordination of support and had to refer every action to Quang Tr¸ Solutions, therefore, were worked out on the basis of expediency, requirements and good will. In addition, the Airborne Division complained that there was only one forward air controller aircraft for the entire area covered by the division. Since the airborne division was involved in several operations simultaneously conducted in different directions this represented a major handicap. This problem was quite evident during the battle at Fire Support Base 31.
Counterattacks by the enemy revealed the weakness of ARVN anti-
tank weaponry. The Airborne Division reported that the M-72 light
anti-tank weapon was ineffective against armored vehicles which
continued to move after being hit. Lieutenant General Lam
immediately notified the Central Logistical Command. As a result
over 300 3.5" rocket launchers with ammunition, all previously
considered obsolescent and placed in storage
A number of units also failed to carry adequate clothing when this was a period of lingering cold in the mountains and forests of the Truong Son Rang© The Central Logistic Command was required to have field jackets and blankets air delivered to units during combat.
Tchepone Was the ObjectiveAfter capturing and destroying Fire Support Base 31, Communist forces continued to encircle and harass ARVN fire bases. North of Route N÷ 9, Fire Support Base 30 continued to bear the pressure of heavy artillery attacks each day and was cut off from the rear by an almost impenetrable air defense net. The ARVN armored task force which tried to pick up the survivors of the 3d Airborne Battalion from Fire Support Base 31 was repeatedly engaged by NVA armor-supported infantry.
South of the road, the targets of enemy encirclement were Fire
Support Base Hotel 2, seven kilometers southwest of Landing Zone
Don, and the 2/3 and 3/3 Battalions of the 1st Infantry Division on
mobile operations along Route 92 nearbÜ On 27 February, despite
heavy air strikes which attempted to silence enemy air defense
guns, a big H-53 helicopter was hit and exploded in the air while
trying to sling-carry a 105-mm howitzer. It was then decided to
close Fire Support Base Hotel 2 and send the 3d Regiment
northwestward on a mission to interdict and disrupt Route 914.
This plan could not be carried out immediately because there still
remained a battery of 105-mm howitzers whose
The situation by this time was becoming increasingly tense throughout the area of operations Truck convoys were frequently attacked on Route N÷ 9 in Laos and on the RVN territory, the enemy increased efforts to ambush convoys and attack rear bases The ARVN westward drive was stalled. In the midst of this situation, I Corps Headquarters received a directive from President Nguyen Van Thieu to have the Marine Division relieve the Airborne Division. He must have realized that such a relief under the combat conditions on that battlefield would be very hazardous. Besides, the Airborne Division was still a strong unit; it had suffered some losses but these losses were not yet too serious. What then caused him to order its replacement? The most probable answer could be that he was really worried over the additional losses that the Airborne Division would sustain in protracted combat. He certainly would like to keep this elite unit intact at all costs. In any event, the Marine Division was a poor choice for the relief. Despite the combat worthiness of its individual brigades, it had never fought as a division.
It was probably with this bothering thought that in the afternoon
of 28 February, Lieutenant General Lam flew to Saigon with an
alternative to present to the President. During his meeting with
President Thieu, Lam's plan was adopted. Instead of the Marine
Division, the 1st Infantry Division with three regiments under its
command was selected to proceed northwest from its present
positions to occupy
Tchepone, a tiny town whose civilian population had fled long ago, now had only scars and ruins left. By this time, it had become more of a political and psychological symbol than an objective of practical military valu© There was nothing of military importance in the ruined town; enemy supplies and war materiel were all stored in caches in the forests and mountains. Lines of communication were located east and west of Tchepone, not in the town proper. Despite all this the Tchepone road junction was near the center of NVA logistics activity in the Laos panhandle and it was understandable that it became a symbol of great importance. The RVN information agencies, the press (both foreign and domestic) all contributed their share in making Tchepone the place to reach at all costs so the ARVN effort now seemed to be more directed at setting foot in Tchepone than trying to destroy the NVA logistical system which was the real objective of the offensive.
Meeting with Ambassador Bunker and General Abrams in the afternoon
of 1 March, President Thieu made known his plan to relieve the
Airborne Division and expressed his desire to helilift two infantry
regiments into the areas surrounding Tchepone. He also disclosed
that the JGS/ RVNAF had been ordered to reinforce I Corps with a
number of tanks and that the Marine Division had been sent to the
northern front. General Abrams took this opportunity to defend the
U.S. position in the face of Senator Tran Van Huong's complaints
that the U.S. was not providing adequate support to RVAAF forces
operating in lower Laos. These complaints had given rise to all
sorts of rumors speculating on the difficulties ARVN forces
encountered in lower Laos. President Thieu stated that the change
of plan did not result from losses sustained by the Airborne
Division but came about because the 1st Infantry Division was more
familiar with the lower Laos terrain and, being an organic unit of
I Corps, was more accustomed to working with the corps and would
respond better to the I Corps commander during this difficult
operation.
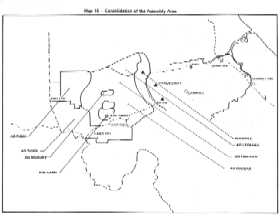
More RVNAF forces were also committed to the new effort. The command section of the 369th Marine Brigade and support elements were airlifted directly to Khe Sanh beginning on 1 March and this movement was completed two days later. The 2d Infantry Regiment was readÜ The 4th and 7th Armored Squadron of the 1st and 2d Infantry Divisions were brought in to reinforce armored elements in lower Laos. I Corps Headquarter����������������������s also relocated the 77th Border Ranger Battalion (+) from Quang Tin and reassigned it to provide security for Fire Support Base Ham Nghi, freeing other forces for combat and the corps' tactical control CP there was strengthened.
While these preparations were made for the push into Tchepone
there were increasing reports of enemy armor presence throughout
the area of operation. In the early morning of 1 March, C-130 gun-
ships
Meanwhile, in the north, the 17th Armored Squadron was heavily engaged and Fire Support Base 30 of the 2d Airborne Battalion remained under sieg© At Fire Support Base 30, fierce fighting took place on 3 March from 0100 to 0900 hours. After heavy attacks by fire, enemy infantry, supported by armor, approached friendly positions. The base was located on a high mountain with steep slopes and enemy tanks were used only to provide direct fire support. C-130 gunships and two Arc Light strikes diverted at the last minute helped the 2d Airborne Battalion hold its ground. When the gunfire ended, a search around the base produced 98 enemy bodies, 26 AK-47s, eight B-40s and two machine-guns right on the perimeter of defense. Friendly casualties were one killed and four wounded. However, as a result of repeated enemy attacks by fire during the preceding days, all 12 artillery pieces (six 105-mm and six 155-mm) had been damaged. In the afternoon of 3 March, the 2d Airborne Battalion was ordered to abandon its positions and move out to evacuate its wounded and conduct mobile operations. The damaged artillery pieces at the base were destroyed before the battalion left.
During the night of 3 March, the 17th Armored Squadron, reinforced
by the 8th Airborne Battalion, engaged a battalion size enemy force
five kilometers north of Ban Dong. Results of the battle were 383
enemy killed two detained, 71 individual and 28 crew-served weapons
seized. Friendly forces suffered over 100 killed and wounded and 10
armored vehicles damaged. In the early morning of 4 March, after
two re-supply and medical evacuation attempts had proved
unsuccessful because of heavy enemy fire, an Arc Light strike was
made and, following it, a third attempt succeeded in evacuating 77
airborne wounded. Only one UH-lH helicopter was shot down and an
airborne company was brought in as reinforcement. The next day, a
column of armor-supported airborne troops linked up with the 17th
Armored Squadron to re-supply it and evacuate
On 2 March, the 7th Marine Battalion, 147th Brigade, began landing troops in Fire Support Base DeltÕ The 2d Battalion of the 3d Regiment, which had suffered from combat attrition at Hotel 2, was sent to the rear to reorganize while other elements of the regiment moved out to operate in the areas of Delta 1 and Brown. For three consecutive days, the 147th Brigade Headquarters and the remaining 2d and 4th Battalions were inserted into DeltÕ Immediately thereafter, the 2d and 4th Marine Battalions moved out to operate in the area of objective AlphÕ The entire 258th Brigade, meanwhile, was inserted at FSB Hotel. The 8th Battalion assumed security of the base and operated in the Co Roc area while the 1st and 3d Battalions searched for the enemy in the area of objective Brav÷ Marine activities during this time resulted in 361 enemy killed and 51 weapons seized. Also, 153 enemy personnel killed by air-strikes were found by marine troops.
On 3 March, in execution of the plan to enter Tchepone, the 1st
Battalion of the 1st Infantry Regiment was inserted at Landing Zone
Lolo 13 kilometers southeast of Tchepone. The landing had met with
strong enemy opposition and had been postponed twice because of
additional preparations required for the landing zon© The 1/1
Battalion finally touched ground at the price of 11 helicopters
shot down, 44
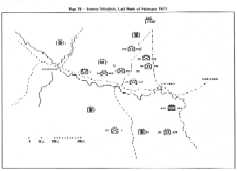
In the morning of 5 March, in order to continue its westward push,
the 2d Infantry Regiment of the 1st Division was scheduled to
occupy Landing Zone Sophia, four-and-a-half kilometers southwest of
Tchepone at 1100 hours but unexpected bad weather delayed the
operation. After preemptive air-strikes, at exactly 1320 hours
five UH-lHs landed safelÜ Sporadic gunfire was received but posed
no major threat. By nightfall, Landing Zone Sophia had eight 105-
mm howitzers in position with adequate ammunition. Searching
further out the 4th and 5th Battalions found the bodies of 124
enemy troops and seized 43 AK-47s, nine 12.7-mm machineguns, four
RPD automatic rifles, nine B-40 rocket launchers, three radios,
military clothing, equipment and food supplies. After securing
Fire Support Base Sophia, the 2d Regiment was now in a position to
control Tchepone from its mountain base and keep the areas
surrounding the town within range of its artillery.
In the afternoon of 6 March, Khe Sanh received an attack by fire of an estimated 22 rounds of 122-mm rockets and two U.S. troops were killed and 10 wounded. Elsewhere, the enemy appeared to take no significant initiative but he was increasing his use of surface- to-air missiles in lower Laos. Earlier, on 2 February, a Mohawk aircraft flying west of the demilitarized zone reported an unidentified missile fired from the ground which exploded approximately 100 meters away, causing no damage to the aircraft. Subsequently, 14 instances of surface-to-air missile firing were photographed or reported by forward air controllers, army pilots, tactical air and reconnaissance aircraft. Missile transportation equipment and antenna vans along with other equipment related to surface-to-air missile systems were also sighted in the tri-border areÕ
The day selected to enter the ultimate objective, Tchepone, was 6
March. A total of 120 U.S. helicopters were assembled to carry out
the assault. In addition to B-52, U.S. tactical air strikes or air
cover sorties were scheduled every 10 minutes. Elements of the
2/17 U.S. Air Cavalry reconnoitered targets, prepared landing zones
and covered the assault. An enemy attack by fire on Khe Sanh Base
forced the huge assemblage of U.S. helicopters to depart 90 minutes
earlier
(1) After-Action Report on LAM SON 719 dated 1 April 1971 by Colonel Arthur W. Pence, pp. 7, 8. (2) Specific instructions from COMUSMACV prohibited any U.S. Army elements from entering Laos in advance of the RVNAF border crossing. (3) Bomb damage assessments were extremely difficult and hazardous to conduct in this dense, heavily defended areÕ As a consequence, only 10% of the B-52 targets struck during LAM SON 719 were reconnoitered later on the ground and even those that were entered by ground troops were so torn up by craters and splintered trees that accurate assessments were impossible. Nevertheless, by putting together all sources of information - prisoner and rallier interrogations, aerial - observation and photography, ground reconnaissance, document exploitation, agent reports and communications intelligence analysts concluded that enemy losses to U.S. air attacks were substantial. (4) Message 00843, 141435Z Feb 71, COMUSMACV to CJCS. (5) Colonel Nguyen Van Tho, commander of the 3d Airborne units routinely secured their fire support bases in this manner. Other ARVN units also employed this technique when the terrain and enemy situation made it appropriate. (6) Colonel Nguyen Van Tho, commander of the 3d Airborne Brigade, was forced by the Communists to make a radio statement denouncing LAM SON 719 shortly after his capture. (7) English names were chosen for objectives, fire-bases and the like primarily to facilitate communications with U.S. support units. During the First Indochina War. The French had followed a parallel practice (at Dien Bien Phu, for example). Perhaps feminine names were selected to bring some softness into the virile world of combatants at war. "Lolo", "Liz", and "Sophia" were chosen by Colonel Vu Van Giai, the very effective deputy commander of the 1st Division who assisted in maneuvering the division during this period. He had served for several years in the DMZ area, in coordination with U.S. combat units, and he naturally followed their practice in naming fire-bases. The small return that the NVA might have enjoyed by exploiting these names for propaganda value - as proof that the Americans were still in charge despite Vietnamization - was certainly overridden by the practicality of having words the Americans could understand and pronounce.
|